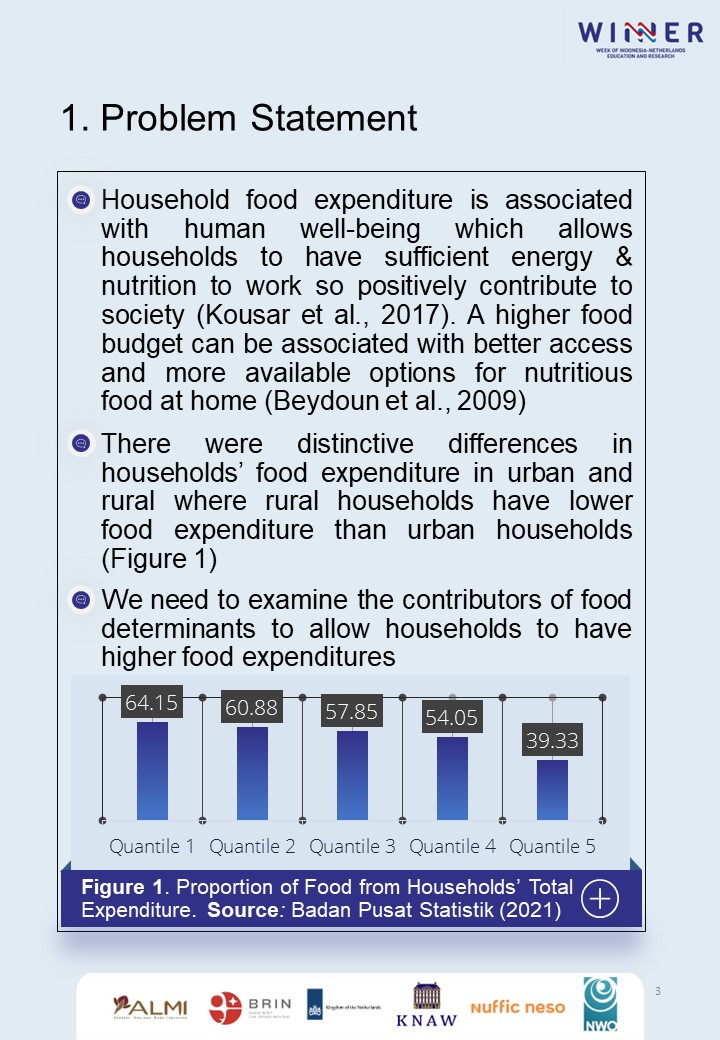
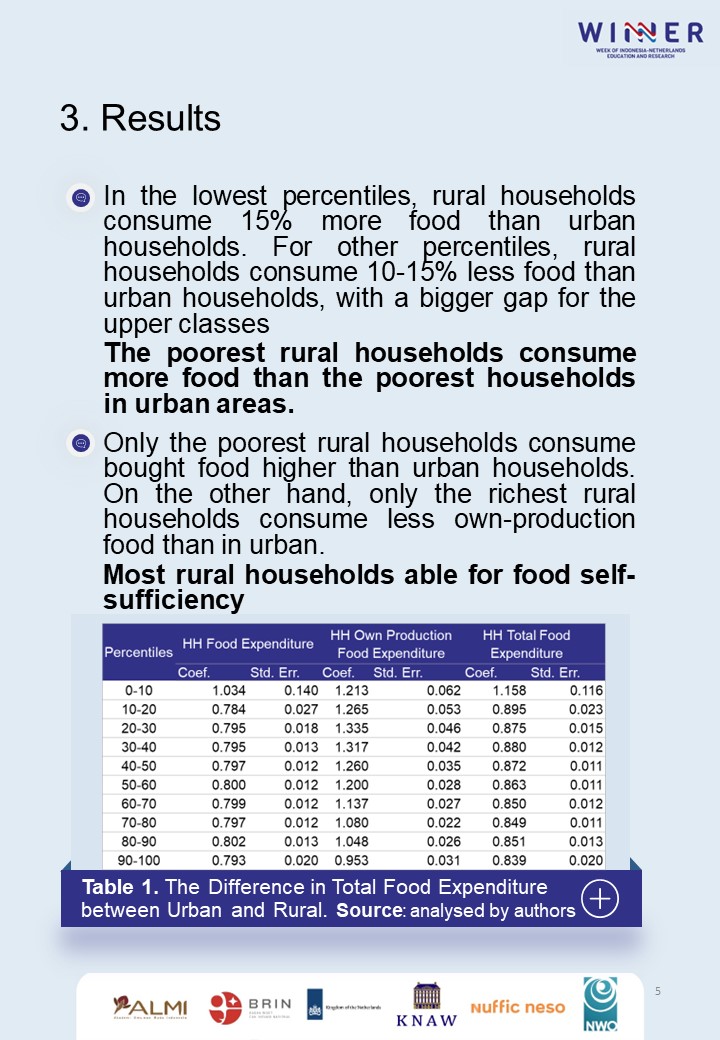
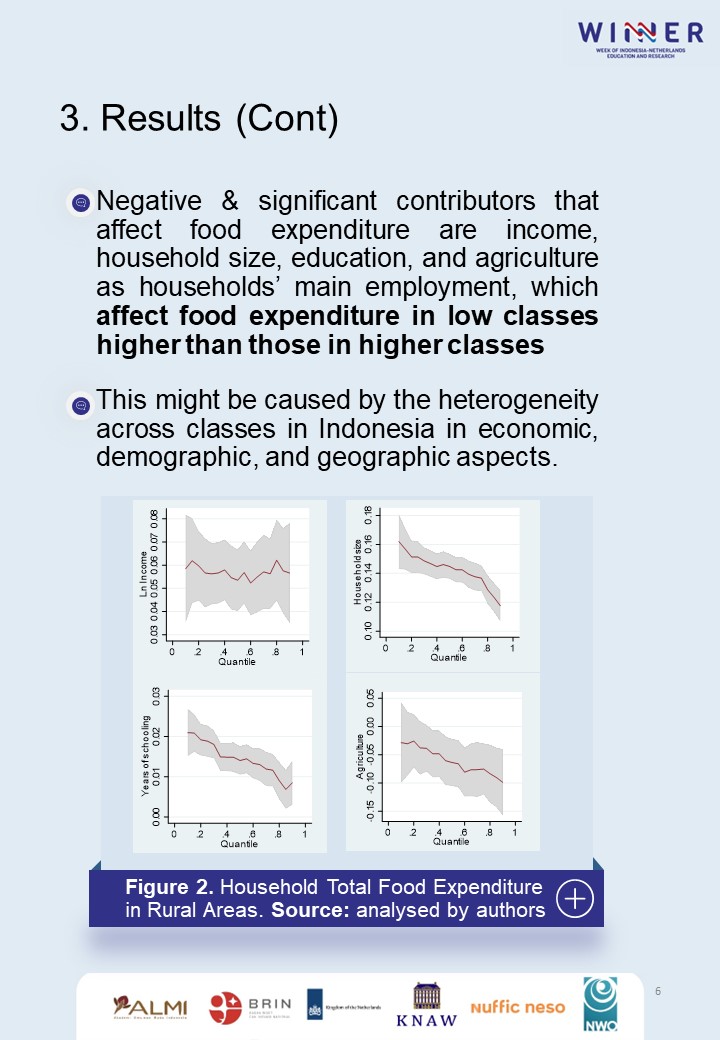
People who live in rural areas have a higher possibility of facing food insecurity than households in urban areas. This condition can lead lack of nutritious food, hunger, health deterioration, and potentially affect their ability to increase human development. Investigations to find the determinants of food expenditure are beneficial for households to allow them to have knowledge on a nutritious diet and give policymakers’ attention to sustainable agriculture. This paper applies quantile regression to investigate potential factors of food expenditure as it can observe heterogeneity across classes and uses IFLS dataset. The results shows that poorest rural households consume more food than the poorest in urban. On the other hand, most rural households able to food self-sufficiency. Some important determinants that can affect food expenditure are income, household size, education, and agriculture as the main employment sector. This paper suggests the need to promote own food production for households, promote population control, enhance education and infrastructure.